Aden
| Republic of Aden Jumhuriyet Aden - جمهورية عدِن | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||
| Motto: "Ahadoun Ahad - أحدٌ أحد" One God, One God | |||||
| Anthem: In The Name of God - باسم الله | |||||
| Capital | Aden Mdin | ||||
| Largest city | Aden Mdin | ||||
| Official languages | Mazanic | ||||
| • National languages | Adenian Mazanic, Mazanic | ||||
| • Regional languages | Allynian, Asani, Masayi | ||||
| Demonym | Adeni | ||||
| Government | Imani Presidential Republic | ||||
| • President | Adnan Mohamad | ||||
| • Vice-President | Hussain Saïd | ||||
| Area | |||||
| • Total | 77841 km2 30054 sq mi | ||||
| Population | |||||
| • Estimate (2021) | 21,230,600 | ||||
| • Census (2019) | 20,527,430 | ||||
| • Density | 263.71/km2 683.02/sq mi | ||||
| GDP (PPP) | |||||
| • Total | 1.07 Billion | ||||
| • Per capita | 52,223$ | ||||
| HDI (2019) | 0.901 very high | ||||
| Timezone | +3 | ||||
| Currency | Dinar (DA) | ||||
| Drives on the | right | ||||
| |||||
The Republic of Aden (جمهورية عدِن, Joumhouriyet Aden), commonly referred as Aden is a country in south West Uletha. It is bordered by Mazan from the northern east, UL02g from the northern west, Alliria from the east, Arion from the south, and The Sea from the west. The capital city is Aden Mdin (also spelled ^Aden Mdin), which is a coastal city located in the coastal center of the country.
Loading map...
The Rich Lands of Aden close to the main cities of Mazan contributed to its rich history which shaped a cultural identity of ethnic diversity. Aden is of 77,823 km2 which includes Mediterranean mountains and coasts and a savannah inlands. The earliest evidence of civilization in Aden dates back more than three thousands years which is why most of its history is found. Aden was home to the Asanians, an old civilizations that took place on the mountains of Aden. The Masayas are an Allirian tribe that was and still is located in the mountains. In the same era, Mazanians came to Aden and declared it as part of their empire which was the main reason of the Imanization of Aden. Most of the Asanians have had close relationships with the Mazanians which contributed into making the New Aden. Few kept the cultural aspect of the Asanians that stayed in the mountains while the territories next to the sea became more and more civilized and educated. The Allyunian savannah was acquired into the territory of Aden in the 20th century. These tribes known as The Allynians enriched Aden's cultural diversity. Aden is one of the most important countries in the Imani world, it is known one of the centers for Traditional Imanis in the world. The economy is enriched by the religious tourism that is mainly due to the important Imani Universities in Aden in addition to its rich Imani history.
Etymology
The word Aden is based on the Aden Bay in which the capital Aden Mdin is centered now. Aden Mdin used to be called Aden before acquiring the name Aden for the country, thus, the addition of Mdin which means city to the name of the city. Aden is derived from Aden. it is not certain on the origin of the name. A theory suggests that the name is based on the "The ^Aden Paradise" in the Imani religion, thus, the Hararis named the city "Aden" as a place in which someone works to go in the afterlife to The Paradise of ^Aden. The name was not named to consider the area as a paradise but a way to paradise. Another theory considers that ^Aden is derived from ^Adnan, the central grandfather of the Mazanics. This theory considers that the Mazanics named Aden the city in memory of their grandfather. Both theories are considered as valid in modern-era Aden, as Aden is considered as a religious country from one side, and that accepts the Mazanics as one of their ancestors.
History
Antiquity
There is evidence that date back to an early settlement in Mount-Asan considered as one of the oldest continuously inhabited areas in West Uletha. The evidence date back to the 1st century. Other evidence suggest that many tribes have settled in nowadays the Allyn savannah. Theory suggests that after a war between the tribes based on ethnicity and discrimination, The Masayas immigrated to the Mount-Ousayn which had no settlements, that theory dates back to the 2nd century.
Asan Sultanate (589-898)
The first known rule in Aden is the Asan Sultanate. The Sultanate is based on an agreement known as the Agreement of Surviving. It was made by the different Asanian families living in Mount-Asan which included the unification of their forces and the establishment of a Sultanate that is centered in Asan. It was agreed on verbally in 589 because of the illiteracy of the Asanians back then. in 656, Sultan Sam The Great was the first Sultan to adhere to Iman This move led to a wide conversion to Iman in Asan though many Asanians kept some of their traditions that weren't fully coherent with Iman. It is suggested that by 657, 90% of Asanians became Muslims.
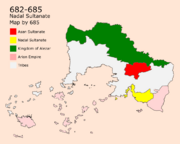
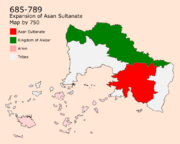
In 682, a small Sultanate was established in Nadal called the "Nadal Sultanate" by Al Nadaly. Al Nadaly is known as a national hero in Nadal. In 2 years, Al Nadaly formed a strong religious population on the coastline of Nadal and made Nadal an economic center in southern Ghetoria. Asanians felt that their importance next to the Nadal Sultanate is diminishing in relation to trade and farming which led them to poison Al Nadaly. His Grand Vizier Joubri took charge while being backed by the Asanians. This led to a revolution of the Nadalians in 685 that ended the Nadal Sultanate. Assanians were already planning an invasion of Nadal. The Asan Sultanate was based only on Mount-Asan until the expansion that happened in 695 that included Nadal, the West, and the area known today as Harar.
Years between 670 and 720 were known as the grand immigration years. After Asanians adhered to Iman, Mazanic were welcomed in the area. The Mazanic language started to be used widely since Asanians were illiterate and found the Mazanic language as an important way for them to be civilized. The immigration led to the habitation of coastal areas in nowadays Aden. This trend has stopped after the plague hit Mount-Asan in 720. It is determined that the plague killed more than half the Asanians at the time. The plague was the main reason of the delay of the Mazanic conquest of Aden. It also scared the Mazanic which stopped the immigration. The plague mostly affected the Asanians and did not affect the Mazanics greatly, causes are still unknown till today, some studies suggest that the Mazanics had great techniques of socially distancing themselves from anyone that had the plague which stopped its spread.
The plague weakened the forces of the Asanians which led to to a civil war inside Asan in 722. However, Asan did not lose control over the territory. This war led to a lot of male deaths which led to many women losing their husbands and it affected the social gender balance thus increasing the amount of homo-amorous women that wanted to find affection and only found women for that. The aspects of this is still found in some areas in Asan were it homo-amorous relationships is still normalized until now even though it goes against Imani culture. Results consisted of a weakened system of governance and a lot of poverty for more than 50 years.
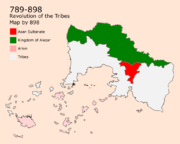
Followed by that, in 789, Sultan Lahab reigned following many failures in governance. Lahab started to reimburse many traditional mores that go back to Asanians before adhering Iman. He believed in a supremacy against the Mazanics and The Nadalis which led into a series of discriminatory events that eventually started the Revolution of the Tribes in 780. Its results was the independence of Mazanis, some Asanians, and Nadalis tribes. In 828, the Second Great Death took place in Asan which led to a great economic crisis in the area, however, it did not affect territories outside the Sultanate. by 898, the Asanians discrimination became excessive towards outside tribes which led to the tribes asking for help from the Mazanics which fastened the Mazanic conquest in the Area.
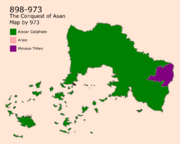
The Alezar Rule (898-1495)
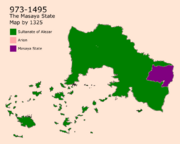
898 was the year the Land of Asan started being officially ruled by the Alezar Caliphate. The Rule included all modern Aden excep Mount-Ousayn which were still governed by tribes. Mazanics were known as peaceful in general but were known as powerful in war from another perspective. Ousayn City, located between Nadal and Masaya, was first settled by Mazanic Nadalis in the 6th century. It was the main place of communication between Asanians and Masayas for two centuries. The Mazanic rule provoked the Masayas as outsiders in the area which led to tension from the start of the Mazanic rule. In 901, Ousayn was separated into two sides one for the Mazanic and one for the Masayas which escalated into the first war of Ousayn in 910 between both parties that led to the full rule of the Mazanics on Ousayn. A second war started in 925 in which Masayas ruled Kousayr (Old City in Ousayn). This era was characterized by many conflicts between both parties until the war of Bahman in 935 in which The Mazanics started the annexation of the Ousayn area. Masayas felt threatened by The Mazanics which led to the establishment of the Masaya State in 973. The Islands in Southern Ghetoria were invaded by the Alezar Caliphate. This started the immigration into the islands which started the dispute on the Islands with Arion that lasted close to 1,000 years.
The Masaya State received a lot of help from other kingdoms for it to stand against the Imani Caliphate of the Mazanic. The boundaries between both parties got unpopulated for a while because of the conflicts except Ousayn the city that was powerfully secured. in 1002, both parties agreed on meeting which led to the treaty of Ousayn that separated the area in a specified way to avoid conflicts. Peace in general was maintained for three centuries. In 1210, A civil war in Asan started on choosing the ruler of the area that resulted in a lot of deaths. Sultan Said Ibn Mujahid Al Ashmali visited the lands in 1212 to ease the war which led to the Treaty of Ashmal that guarantees the rights of all the parties in Asan. In 1310, the plague revisited Asan killing a lot of the men. The Masayas considered the plague as a chance for them to invade Asan which happened in 1310. Many mosques were destroyed by the Masayas until their withdrawal in 1311 after the Mazanics kidnapped the son of the ruler of the Masayas. After the son of the ruler came back to Masaya, in 1313, The Masayas killed 75% of Ousayins in Ousayn City and the close villages which was known as the Ousayn Genocide. It was followed by another genocide in the Nadal region in 1314. The genocides led to many Ousaynis and Nadalis running away from the sea to save themselves, they stayed in the Nydal islands that is an island close to the inlands but far from Masayans.. Mazanics launched a war against the Masayas that ended with an economic crisis in Masaya that was the start of the collapse of the Masaya State.
Followed by the economic crisis in Masaya, The Masaya rulers accepted help coming from Nadal which led to Many Masayas embracing Iman because of the communication with the Nadalis that wasn't happening before. Between 1356 and 1410, the Imanization of the state increased which led into a revolution on the rulers which resulted in reforms in the ruling. Non-Muslims and Muslims started a civil war in Ousayn in 1410 that lasted for 43 years. In 1453, rulers from both sides agreed on meeting and signing a peace treaty in Nadal.
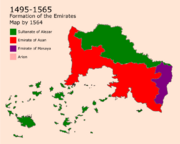
Union of The Emirates (1495-1775)
In 1495, after a decade of negotiations between the Mazanics and The Asanians, a treaty was signed between both parties that concluded the semi-independence of Asan from the Sultanate of Alezar, making it a sovereign entity under Mazanic Influence which resulted in the formation of the Emirate of Asan on 28th of march 1495. By 1512, Masayas became in majority Imanis, thus, they signed a similar deal with the Sultanate forming the Emirate of Masaya on the 13th of April 1512. On 15 march 1565, both rulers of the Emirates met in Ousayn to sign a deal on the formation of a union known as The United Emirates of Asan.
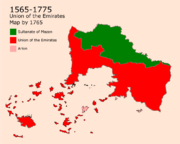
The Era of the Union was known as "The Golden Age" of Asan which was best known by the economic, educational, and culture renaissance. The Imani University in Nadal used to get thousands of students from all around the Imani world especially Arsam. This era was also known as the Harari Imani Era which started by Al Harari, a scholar born in Harar that influenced the coastal areas of Asan. While the coastal area were getting more and more educated and religious, the areas in Asan city were being influenced by Al Asin who was a supremacist that revived the Asanian traditions of discrimination once again. in 1775, a civil war started between both parties that was followed by the Arion invasion of Asan on the 16th of February.
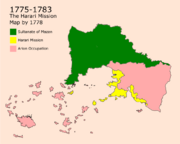
The Arion Rule (1775-1783)
On the 19th of February, Major Harari religious figure met secretly and formed the Harari forces that would become the main opposition of the Hellanesians. by the end of may, Hararis gained their independence in Harar which was followed by many battles against Arion. On the 12th of august, on the lands that are now Aden Mdin, a battle known as The Battle of Aden started between both parties. After the win done by the Hararis, The Hararis liberated most of the coastal areas. A war to liberate Baytrouh followed in 1776 which was a success. in 1778, The Hararis would have already liberated Ousayn.
Arion established a coastal town on nowadays Harbel Mdin where old Imani settlements already existed. This area was known as the center of the war between both parties which is the reason why it was named as Harbel Mdin. On the 18th of July 1778, Arion launched a genocide on the Imanis of Harbel Mdin which led to the war of Harbel Mdin in 1779. The War is still known until today as one of the deadliest wars Aden has ever experienced. Later on, a peace treaty between both parties was signed on the 13th of may in 1779 to division of the cities into two parts, the Imani part governed by the Hararis and a Hellanesian part governed by Arion. Hellanesians are still to be found in Aden and especially in Harbel Mdin which they consider as their capital in the area.
by 1783, the Hararis started a war known as "The Independence War" in which the goal was to free Asan from the rule of Arion. on the 24th of may, a treaty between main Asanian figures and Harari figures was made in Aden Mdin nowadays known as The Peace Treaty of Aden in which all parties agreed on ending the rule of Arion. Arion heard about the treaty and invaded Aden on the 26th of August which led to a battle known as The Second Battle of Aden in which Arion lost and had to withdraw from the area.
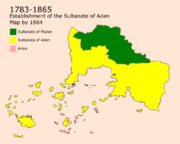
The Sultanate of Aden (1783-1865)
from Aden Mdin, agreement was made on the establishment of a Sultanate centered in Aden named the Sultanate of Aden on the basis of the treaty that happened on the 14th of february in 1784. The Capital was chosen as Aden for it being on the center of the coastline and for it to be different than all the older capitals to avoid any superiority based on ethnicity and history.
The Sultan received a lot of acceptance from all over Aden as the central religious government for the area. This did not last long, as a civil war started between the Asanians and the Masayas in 1801 on the governance of Ousayn which lasted for three years. During that time, Aden lost a lot of its food supply because of great fires that happened because of the sudden change in climate. The huge number of deaths because of the great famine led to a peace treaty that ended the war by 1803. in 1805, huge immigrations of Imani Turquese into Asan happened after a war in the Demirhan Empire, they formed an integrated community based on peace in nowadays known as the Turquese Valley.
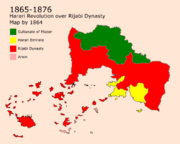
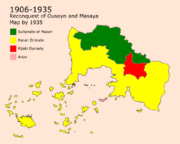
The Harari Emirate and The Rajabi Dynasty (1865-1935)
in 1850, Sultan Rajab El ^Omari reined the Sultanate, he was known as one of the reformers that modernized the country and integrated some of the lost culture of Arion that did not oppose Imani beliefs which led to improving the relation of Aden with major non-Muslim kingdoms in the world. A coup-d'etat happened in 1865 after the death of the sultan, it was led by his son Rajab Ibn Rajab. He did a major amendment that changed the electoral system of the sultanate into a dynasty in which the son of the sultan follows him after his death. This led to major protests all over the country that Rajab fought by blood which led to many people getting killed by the Rajabis.
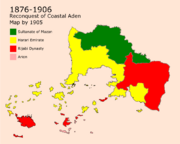
The Hararis were the main group that did not accept that change because of it being against the rulings of Iman. However, the Hararis did not take part of the revolution, they started to meet secretly to plan on regaining independence all over the country. Most of their trials failed until the Harari war of independence that started in 1876 that started freeing areas one by one, the first city to gain independence was Nadal in 1876. Hararis kept on trying until they were able to form the Harari Emirates in the Harar and Nadal area. in 1905, a battle took place in Aden Mdin which led to the liberation of the city and moved the dynasty's capital to Asan. by 1906, the Nydal, Baytoruh, and ^Abdar areas were fully liberated. The most deadly war of the era was the Ousayn War that started on the 24th of February in 1913. The war kept on going until Ousayn and Mount-Ousayn were liberated on the 12th of August 1918. A war launched in 1925 which was the start of the end of the Rashidi Dynasty.
By 1925, the Turquese rebelled against the dynasty in which a three years long war kept on going and led to a lot of deaths between the Turquese people. Conflicts rose between the Turquese that wanted to be part of the Harari Emirates and the close villages that wanted to stay part of the Rashidi dynasty. The Conflict was major because of the close distance between the settlements of the Turquese and the Asanians. in 1928, a civil war between both parties that ended in 1932 by the exchange of citizens between towns of the Asanian villages which led to the segregation that is still present between the Turquese and the Asanians.
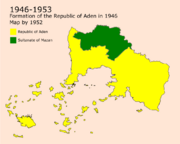
Formation of the Republic of Aden (1936-1953)
In 1933, a revolution in Asan removed Rajab from being the ruler and executed him in what is known now as The Enemy's Square. Asanians formed a small republic on the 15th of November in 1933 called The Republic of Asan. The Hararis did not approve or accept the move done by the Assanians which led to major conflicts that started to ease by the peace treaty of Baytrouh in 1938. The Asanians suffered during that time from an economic crisis because of their land being surrounded by the Harari Emirate which led to the Asanians signing s treaty with the Hararis on the 21st of February in 1941 known as The Treaty of The Republic. This treaty would consider Asan as a semi-independent entity in the Emirates of Harari and includes a reform in the Emirate in which the government would switch to being a republic that is more open to diversity and for it to be for all citizens of Aden, thus, the start of the formation of the First Republic of Aden. Conflicts kept on rising between both parties until the Hararis declared the Republic of Aden in 1946 after annexing Asan and making it fully as part of the republic on the 16th of February.
Modern-Era Aden (1953-present)
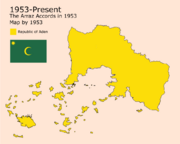
In 1947, while Aden was starting its second renaissance, the Arraz Accords happened between Aden and Mazan in the city of Arraz. This gave the Alezar, Hodoud, and Allyn areas to the republic of Aden because of the presence of Adenians and Allynians in the area.
The Accords were to be effective by 1953 after 9 years of the treaty. No strict border passing will be formed on the borders with Mazan. by 1949, different rulers of different areas in Aden and the rulers of Allynian tribes and the Mazanic Sultan met in Aden Mdin in what was known as The Treaty of The Capital in which a referendum was made on the constitution that specifies the rights of all the parties in addition to adding the territory of the Allyn savannah officially to Aden with Allynians getting special treatments and budgets in Aden. The treaty was signed on the 16th of February in 1950. This day is known as the Aden National Holiday. The referendum was fully endorsed on the 7th of may in 1953 on which The New Republic of Aden was officially formed.
Aden experienced great improvement in its infrastructure during the last decade in addition to a great economic growth which is mainly because of the government that is based on full transparency. By 2020, Aden is one of the most advanced countries in the world and the most advanced country in the Imani world. It holds great relationships with different parts of the world and is considered as the capital of the Imani world. Despite Aden having a small size compared to other major nations, its unity with Mazan, it is considered a major force in the new world .
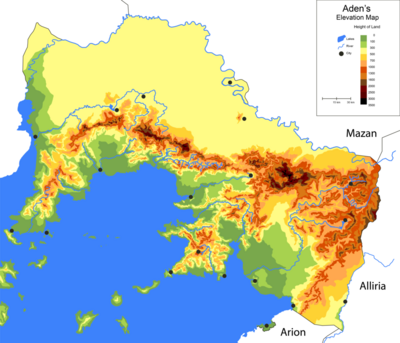
Geography
Aden is located in the southern west of West Uletha, on the shore of the Sea, extending for about 70 thousand sq kilometers. The capital city, Aden Mdin is at the center of the country from the shore, it was initially a small settlement next to the River of Aden but it naturally expanded after the formation of the republic across Aden Bay known historically as The Golden Bay.
Aden is divided into four distinct physiographic regions: the coastal plain, the Aden mountains, the Alyyian Savannah and the Islands of South Ghetoria
The coastal plain which is rich with lands that are suitable to be used as farms, different chain of interior mountains including high peaks. However, The Coast gets very narrow in the Harar and Nydal area. The Mountain of Ousayn included the highest peaks in Aden, with the peak of Masaya (3545 m) as the highest. The Mountain of Asan is known as the heart of Aden because of it's central location in the country and the importance of its territory in older times. Its highest peak is the peak of Asan (3242 m) followed by the peak of the Turquese (2174 m). The Baynal Rayn peak (1765 m) is considered as an important peak because it is very close to the coast.
The Allyn Savannah is in the north of Aden behind. Mount Allyn is a rocky mountain found in the desert next to the city of Allyn, it peaks at 950 meters.
The inland coastal plain includes the coastal area excluding the islands coasts and Maytam's coast. it is 1290km long and includes the capital and major cities.
Islands
Aden has 59 islands and more than 800 islets (44 mapped in OGF). All of them lay in the the Aden-Arion bay. The biggest island (partially part of Aden) is the Inrak Island. Their are 4889.629 Km2 (6.28%). Most of the Islands are settled by Adenians and Hellanesians. There are more than 1,400,000 person living on the Islands of Aden Bay (73% Adenians, 23% Hellanesians, 14% Others). The Biggest city on Islands is Nydal (280,000 person) followed by Inrak (185,000). Inrak is the largest and most populous island and it is split between Aden and Arion. It is 157km away from the closest inland point in Nydal.
The Aden islands are traditionally grouped into the following clusters: the Inrak Islands which are the most far from the coast, Maytam Islands which are disputed with Arion and are bordered by Arion Islands, and the Nydal Islands close to Nydal.
Climate
The climate of Aden is primarily Mediterranean, featuring mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers on the Coast and the mountains. This climate occurs at all coastal locations, including the Islands and the Land of Nadal. The Asan mountain range strongly affects the climate of the country. Topographical variation creates local modifications of the basic climatic pattern. The inner-area's climate is Savannah climate with a special touch of Mediterranean. Fall is a transitional season with a lowering of temperature and little rain; spring occurs when the winter rains cause the vegetation to revive.
In the Aden Mountains the high increase in altitude produces extremely cold winters with more precipitation and snow. The summers have a wider daily range of temperatures and less humidity. In the winter, frosts are frequent and snows heavy; in fact, snow covers the highest peaks for much of the winter. In the summer, temperatures may rise as high as 31 Celsius during the day, but they fall far lower at night. Inhabitants of the coastal cities, as well as visitors, seek refuge from the oppressive humidity of the coast by spending much of the summer in the mountains, where numerous summer resorts are located.
The Allyn Valley have considerably less precipitation and humidity and a wider variation in daily and yearly temperatures.
Rivers
In Aden many rivers flow, which are important in the term of length. There are 21 permanent rivers in Aden (6 in Inrak island and 1 in the Maytam exclave) which are the main source of drinkable water for Aden. Many small rivers meet with other major ones which makes them prominent in the area.
Demographics
Religion
96.01% of the Adenian citizens are Imani. Minorities can be found mostly in Allyn (327,014 non-Imanis), Inrak (97,545 non-Imanis), and Maytam (44,436 non-Imanis). Estimates of the Irfan population of Imanis in Aden range between 75% and 90%. Important religious figures have shaped the population including Imam Mohamad Nadaly (Resided in Nadal) and Imam Al Harari (From Harar in Aden).
Imanis are given priority and importance in Aden which is mainly because of the intensive history of Iman in the country. Religious Studies is considered as a great source of pride in the country which increase the religiosity level of the population.
Languages
Most of Aden's population used to talk Mazanic from antiquity. However, it was not well implemented except after Al Nadaly's settlement in Nadal. Almost everyone in Aden speaks Adenian Mazanic (The Common Dialect of Mazanic). Hellanesian is spoken frequently on the Islands and in Maytam City because of its closeness to Arion. Asani was the official language of Asan until the 10th century, it is still spoken in some mountainous areas of Asan, however, since it is not a written language, it is written with Mazanic letters sometimes as a cultural practice in the Asan area. Most Masayas speak the same language as Allirians as a second language. Turquese is spoken as a first language by the Turquese people.
In business, Ingherish and Mazanic are used accordingly. There are strict rules about the Mazanization of Aden and the preservation of culture and religion which includes the language.
Ethnicity
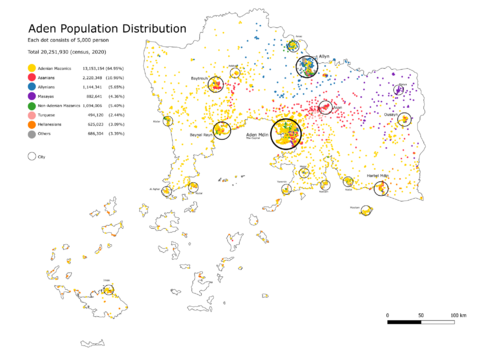
Aden's ethnic composition is heterogenous. According to the constitution, Aden is composed of 6 main ethnicities: Mazanics (including Adenian and non-Adenian Mazanics), Asanians, Allynians, Masayas, Hellanesians and Turquese. 70.35% of Adenians are Mazanics.
Historically, Asanians used to live in the area of Mount-Asan while Masayas used to live in Mount-Masaya. Hellanesian used to be found on the islands. On the other hand, Mazanics used to live on the coast and on the Western inland area of Baytrouh and Ashhad. Even though scientifically Mazanics and Asanians ethnicity is close, historical cultural factors kept them separated.
Distribution of Ethnic Groups
Cities
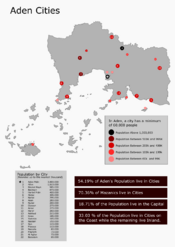
Aden is 54.19% fully urbanized with 11,001,304 living in cities. More than 33% of the population live on the coast with 18.7% of them living in the capital. 81.35% Non-Adenian Mazanics live in cities while only 39.65% of Masayas live in cities which is the lowest percentage between all ethnicities.
The biggest city is the capital Aden Mdin with 3,800,000 residents in the city border. It is followed by Allyn (1,610,000) and Baytrouh (670,000).
Minorities
Asanians, Mazanics, Allynians, and Masayas are all indigenous to the lands of Aden. The borders of Aden are made on the basis of the Historical division that can be traced to the Sultanate of Alezar. On that basis, Asanians, Allynians, and Masayas are not considered as minority groups in any political form in Aden. However, some reports of racism in Asanian lands has been seen against Mazanics and Masayas.
Turquese (2.44%) are treated as part of Aden's indigenous populations even though they are considered as a minority everywhere except in the Asan Valley. Turquese culture has been increasingly trendy in Aden which is a result of the good relation between Aden and Demirhan. Hellanesians (3.09%) have lived on Aden's islands for hundreds of years. Some conflicts have been seen between them and Mazanics but the general spirit is positive in the land.
The newest minority can be considered as the non-Adenian Mazanics (5.4%) as they are all foreigners that moved to Aden in its recent years in contrary to the Adenian Mazanics that have lived in Aden for more than 400 years as a minimum.
According to local agencies, Allyn is considered as the most diverse city with 56% of the population as non-Mazanic (excluding indeginous cities like Asan and Masaya with the majority being minority groups).
Education
Education in Aden is overseen by the Department of Education and is accessible to all the residents free of charge. More than 98.7% of the population know how to write and read. The levels of education for Men and Women are pretty close with no significant differences. Children are required to attend school from the age of about 6 up until about 16.
The education system in Aden is similar to the one in Mazan. It is divided into stages based upon age: Early Years Foundation Stage (ages 3–5), primary education (ages 5–11), secondary education (ages 11–18) and tertiary education (ages 18+). In Imani schools, the secondary stages is shorter (11-14) and the tertiary education starts at 15 years old.
Higher education students normally attend university from age 18 onwards, where they study for an academic degree. There are over 40 universities in Aden, most are public institutions. The Department for Education is the government department responsible for higher education in Mazan. All public universities are free. The first degree offered to undergraduates is the Bachelor's degree, which usually takes three years to complete. Students are then able to work towards a postgraduate degree, which usually takes one year, or towards a doctorate, which takes three or more years. An additional year of "Imani Cultural Studies" is required to enter into any governmental field or educational field. It is required by civil law for all companies to pay an increase of 20% for individuals that have the degree. This degree can only be received from the Imani accredited universities that can be found in most cities.
Law
Minorities
Aden Unity Law
The Aden Unity Law was passed in 1948, it includes the unification of all ethnic groups under an Adenian umbrella. In recent years, this law has been criticized as erasing the cultural aspect of Asanians since it specifically states that some cultural aspects of Asanians is not allowed to be visible outside Asan. This includes that the red color is not allowed to be in any regional flag outside Asan. Review on this law has been contradictory as some thinkers consider it as a way to keep unity and stop supermacy ideologies and others consider it as saving the Asanian culture from being appropriated.
Non-Discriminatory Law (non-LGBT section)
in 1975, the "Non-Discriminatory Law" was passed. This law has been updated in 1983, 1987, 2010. The initial law was issued on the basis of "issuance of clear articles against discriminatory based on ethnicity, culture, race, and richness". This law has been considered as the basic law that saves minorities from discriminatory. Discriminatory actions can be punishable by up to 3 years of prison. The discriminatory law initially did not include any articles in relation to religion. In 1983, an updated version included the punishment of "any actions that can cause conflicts between the population" which intended in minimizing any hate speech that can cause conflicts. However, Adenians are still allowed to hire based on religion and can refuse to hire a non-Imani on the basis of "Purity of the Business". The Discriminatory law has included updates about the LGBT community in 1983,1987 and 2010.
LGBT
Non-Discriminatory Law (LGBT section)
The LGBT section of the law has been introduced in 1983 in order to stop any "extreme discrimination against a person with different preferences". The law included the ban on accusation of homosexuality on any individual without a clear indicator. The law also considered so-called "Pride Killings" without the clear indicator as punishable by death, with a clear indicator, the punishment can vary between 5 to 30 years in prison. In 1987, the law has been updated in order to add specific laws that would consider discrimination in the workplace against "feminine men and masculine women" as punishable by 3 years of prison. This update included other important clarifications on the punishment that might happen on the basis of "sexual activity with the same sex in publics spaces" (this law has included in 2010 any 2nd or 3rd degree of sexual activity between any unmarried couple in public spaces and on the internet).
Sexual Offensiveness Law
The sexual offensiveness law was passed in 1946 in order to criminalize any sexual activity without a legal contract that is done in public. The sexual offensiveness law has been updated in 2005 to include the "claim of marriage between a homosexual couple" as it can be seen as a publicity of sexual activity that is illegal.
The Civil Contract Law
In 2019, The supreme court has issued a Law that allows any two individuals of the same sex to make a civil contract that would allow in "easing the laws against the LGBT members". The civil contract can be made between people above 18 years old that are not married. It is not a marriage but makes it easier for people to share their households and financials together. This law also includes that a person can share 1/3 of his inheritance to the other party.
Adoption
In Aden, Adoption is illegal for any individuals and is not approved by the government. Supporting a child is legal, however, in All of Aden and does not require a couple. This has led homosexual couples to raise children under the "Support System".
Transgenders
It is prohibited and illegal for Adenians to change their sexual appearances in order to be considered as from a different gender. However, it is considered as legal if for "medical reasons". However, discriminatory against transgenders is also prohibited.
Government and Politics
Aden is a presidential republic that includes a major control of the president on the executive, appointing the cabinet, and draw up the budget. Most of his rulings need a 50% approval from the parliament. The Vice-President is also the Prime Minister. The President is elected by the whole population when the position is free. The president can only be dismissed under a 75% vote in the parliament and an approval of the Imani Council. It has been an unofficial requirement for the president to have got the acceptance of the Mazanic Sultan and the Imani Council in Tabah before becoming a President.
The Parliamentary elections happens each 4 years. 200 members are elected by the population. A quota of 20 seats are saved for Asanians and 10 seats are saved for Minorities. There should be a minimum of 50 women in the parliament. The Elections are based on governorates and the seats are divided on the basis of ethnicity (Mazanics, Asanians, and Others). Parties are allowed to compete for the elections on a "non-profit" basis.
Administrative Divisions
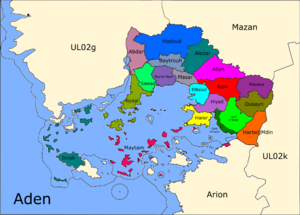
Aden is divided into 20 governorates (محافظة، Muhafaza) with Aden Mdin being the capital and the center for the Parliament. The advisory Aden Imani Council is in Harar with secondary Councils in each Kaza. The 20 governorates are divided into districts (قضاء, Kaza) which are divided into several municipalities. Some municipalities are divided into distinct neighborhoods especially in cities.
| Governorate Name | in Arabic (محافظة) | Postal abbrev. |
Governorate Capital | Area (km2) | Population | Pop.
Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ElBalad | البلد | BLD | Aden Mdin | 2,448 | 4,350,000 | 1,777 |
| Allyn | ألّين | ALN | Allyn | 5,550 | 2,300,100 | 414,43 |
| Baynal Rayn | بين الرين | BRN | Baynal Rayn | 2,779 | 2,150,000 | 773.66 |
| Baytrouh | بيتروح | BTR | Baytrouh | 3,044 | 1,650,300 | 542.15 |
| Asan | أسان | ASN | Asan | 4,298 | 1,400,500 | 325.85 |
| Harar | هرر | HRR | Harar | 2,448 | 1,320,000 | 539.22 |
| Harbel Mdin | حرب المدين | HRM | Harbel Mdin | 4,162 | 850,200 | 204.28 |
| Ousayn | أُسين | OSN | Ousayn | 4,363 | 765,000 | 175.34 |
| Abdar | عبدر | ABD | Abdar | 4,405 | 750,300 | 170.33 |
| Nydal | نضال | NDL | Nydal | 4,335 | 730,500 | 168.51 |
| Coast of Nadal | ساحل ندال | CND | Nadal | 1,092 | 685,000 | 627.29 |
| Inrak | إنرآك | INK | Inrak | 3,405 | 650,300 | 190.98 |
| Alezar | العزار | AZR | TBD | 5,067 | 505,300 | 99.72 |
| Hiyad | حياد | HYD | Sayouban | 3,077 | 450,200 | 146.31 |
| Masaya | مسايا | MSY | Masaya | 4,524 | 423,530 | 93.62 |
| Maytam | ميتم | MYT | Maytam | 2,268 | 370,300 | 163.27 |
| Sawad | سواد | SWD | TBD | 3,054 | 340,300 | 111.43 |
| Hodoud | حدود | HDD | TBD | 10,976 | 320,400 | 29.19 |
| Masar | مسار | MSR | TBD | 1,865 | 300,200 | 160.97 |
| Land of Nadal | سهل ندال | LND | Wassina | 4,681 | 215,000 | 45.93 |
Foreign Relations
Aden has great relations with Mazan. Both share open borders and great trading agreements. Both countries have open borders together. The relationship can trace back to the Sultanate of Alezar. Aden enjoys good relations with all other countries with Imani majority populations. Aden also enjoys neutral relations with Arion and Alliria (its neighbors), however, they do not have open borders. In the 1800s, many conflicts arose on the borders. Also, All Imanis in the world have access to Aden Visa-Free if they can prove their belief in Iman.
Military
The Aden Armed Forces (A2F) has 210,000 active personnel, including 3,100 in the air force, and 2,500 in the navy.
The Aden Armed Forces' primary missions include defending Aden and its citizens against external aggression, maintaining internal stability and security, confronting threats against the country's vital interests, engaging in social development activities, and undertaking relief operations in coordination with public and humanitarian institutions.
Aden is a major recipient of foreign military aid given by Mazan.[188] With more than $1 billion since 2010, it is the largest per capita recipient of Mazanic military aid.
Economy
Agriculture and livestock
Industry
Oil and Gas
Energy
Services
Tourism
Transportation and Infrastructures
Roads
Railways
Urban mass transit
The cities with a subway system are:
Air transport
Waterways
Health
Culture
Anthem
The National Anthem of Aden (Mazanic: نشيد عدِن الوطني, Nashid ^Aden Al-Watani) was written and composed by Omar Ibn Mohammad in 1803. It was formally known as the Anthem of The Sultanate (Mazanic: نشيد السلطنة, Nashidoul Saltanah). It was adopted on the 16th of February 1953 during the treaty of the capital.
History
When Omar Ibn Muhammad wrote the anthem during the Sultanate, the Sultan back then loved it and asked for all mosques to read it after every single prayer, this led to the anthem being memorized by most of the population. The Anthem had a special place in the nation, Adenians used to recite it in their weddings, their funerals and whenever they are happy.
In 1953, during the treaty of the capital, The anthem was adopted as the national anthem because of its special place for the citizens of Aden.
Lyrics
| The National Anthem | ||
|---|---|---|
| Mazanic | Adenian Mazanic | Ingherish Translation |
| <poem>باسم الله
بسم الله الرحمن راحمني في دنياي وآخرتي بسم الله الهادي هداني إلى الصراط المستقيم يا رحيم يا رحيم الله يا الله لك الملك وإياك نعبد باسمك ربي نحكم باسمك ربي نعدل نسألك الحكمة نسألك العدل نسألك الأمان نسألك الغفران أحدٌ أحد أحدٌ أحد في السلام وفي الحروب باسمك ربي نخوض البحور </poem> |
<poem>Bismillah
Bismi l-Raḥman Raḥimouni Fi Dounyay wa 'akhirati Bismillah l-Hadi Hadani 'ila Sirat-in mustaqim Ya Rahim Ya Rahim Allahou ya Allah Laka l-moulk wa 'iyyak na^boud Bismika Rabbi Naḥkim Bismika Rabbi Na^dil Nas'alouka l-ḥikma Nas'alouka l-^adl Nas'alouka l-'aman Nas'alouka l-ghofran Ahad-oun Ahad Ahad-oun Ahad Fi l-salam wa fi l-ḥouroub Bismika Rabbi Nakhoudou l-boḥour </poem> |
<poem>In the name of God
In the name of The Most Merciful The One that has mercy on me in my life and afterlife In the name of God the one who guides me The one who guides me to right path O The Merciful O The Merciful Allah O Allah To you we belong and we worship you In your name God we rule In your name God we are just We ask You make us wise We ask You to make us just We ask You to grant us safety We ask You to grand us forgiveness You are One and Indivisible You are One and Indivisible In peace and In war In your name we cross the seas </poem> |