Ambrosia
| Ambrosia Ambroisie | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Loading map... | ||||
| Capital | Port Ambroise | |||
| Largest city | Meridian | |||
| Official languages | Valonian | |||
| • National languages | Lentian, Native Archantan | |||
| Ethnic Groups | Ulethians (72%), Balthuks, Amiscoux, Rodes, Ascubecs, Hachalaggans | |||
| Demonym | Ambrosian | |||
| Government | ||||
| • | Roland De Léon | |||
| Area | ||||
| • Total | 228 326.93 km2 88 157.52 sq mi | |||
| Population | ||||
| • Census | 7 783 515 | |||
| • Density | 35/km2 | |||
| Timezone | +8 | |||
| Currency | Ambré (Æ) ((AMB)) | |||
| ||||
Ambrosia, Ambroisie (in Valonian), Ambrozijn (Lentian), is a country located on the Southwestern coast of Astrasia. It is bordered to the South by the Asperic Ocean, to the East by Ardencia and by Deodeca. Its capital is Port Ambroise but Meridian (Méridrien / Meridiaan) is the largest city. The country covers a land area of 228 326.93 km² (88 157.52 sq mi) and has a population of about 7 millions people (Ambrosians).
Etymology
Ambrosia bears the mythologic name given to the food of the gods which was supposed to confer immortality. Ambrosia is also the name of a plant widely present in the south of the country and was certainly the reason why this last one has been named this way.
History
To be determined but it was certainly a former Valonian colony, maybe it still... Was part of the former the Valonian Asperia Colony in Southern Astrasia.
Geography
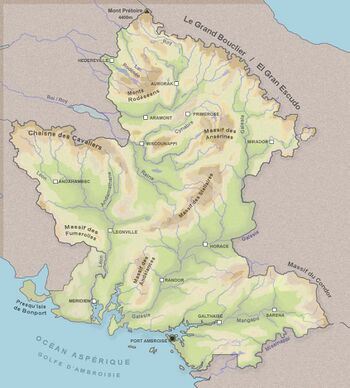
The territory of Ambrosia is located between the 40th and 46th parallel south and between the meridians 128 and 135. Covering an area of 228 326,93 km², it has a rich geographical diversity and can be divided into three large distinct regions Lower Ambroisia, territory on which the main rivers flow towards the South, Upper Ambrosia where rivers flow towards the northeast on the east side of the Galese River. The borders are mainly materialized by the natural relief. The Great Shield mountains in the North separates Ambrosia from Deodeca and the Cavaliers chain separates western countries. A group of hills define the boundary between Ambrosia]] and the northwest. The central part of the course of the Galese River marks the border with the southern part of Deodeca and The Missanappi River, the border with Ardencia.
The geographical extremes:
The Cap Meridion is the southernmost point of the country is located at the end of Meridion Island [1]. Mount Preatorium (Mont Prétoire)[2] is both the northernmost point and the highest one (4400m) of the country. Mount ... (1984m) in the Condor Massif (Eastern Galesia) materializes the most eastern point of the country [3] and Mont Saint Just (Sint Juust) the most western one.
The Galese River is the longest river with 920km and the Lake Rodezee the largest body of water.
The coast:
The country is bordered on the south by the Asperic Ocean which penetrates deeply into the lands forming three long inner bays :
- Meridian Bay between the Admiral Cape (Cap de l'Amiral / AdmiraalKaap) and the Lanterns Cape (Cap des Lanternes / LantaarnsKaap).
- Bay of Isles (formely Onkavik Bay) between the Admiral Cape (Cap de l'Amiral / AdmiraalKaap) and the Horanggan Peninsula.
- Galthaise Bay
The Islands : The coast and the bays are scattered by many islands and islets of different sizes. Some of them are populated.
-The Nectarydes Archipelago represents a group of four main islands (Bordanse, Langeiron, Andreade and Astrel)[4] all are connected to the coast from Miramar harbour.
-Santandrian Island is the largest island. It is located in the Bays of Isles [5]
-Sleutel Islands
-Meridion Island is the southernmost island [6]
Ranges of mountains : Ambrosia is generally pretty hilly, more mountainous in the North and flatter in the South East in Galesia.
The Andelances [7]
The Anserines
The Great Shield (le Grand Bouclier) : Its highest, peak Mount Preatorium (Mont Prétoire) culminates at 4400m and marks the border between Ambrosia and Deodeca. [8]
The Cavaliers (De Ruiters) [9]
The Massif des Flamboyants
The Massif des Fumerolles (Fumarolen Massief) [10]
The Rodesian Mountains [11]
The Massif des Stellaires [12]
The Condor Massif [13]
Lakes and rivers:
The Galese River (le Galèse) is the longest river (920km).
The Leon River (le Léon / de Leeuw) is the second one
The Indigo River (l'Indigo)
The Mekoha River (le Mékoha)
The Kerohan River (le Kérohan)
The Missanappi River (le Missanappi)
The Lake Rodezee (le Lac Rodézée)[14] is the largers lake.
The Tabaskinac Lake
The Avondmaal Lake
The Ronceval Lake
The Saune Lake
The Sandrin Lake (le Lac Sandrin)
Climate
Ambrosia is located in a temperate zone, partly under oceanic and continental influence as we approach the mountain ranges. Lower Ambrosia is mainly a region with an oceanic climate with prevailing winds from the south-west giving frequent rainfall and mild temperatures with few annual amplitudes, whereas Upper Ambrosia has a more continental climate and benefits, in plain, from summer temperatures warmer, but its higher relief and higher average altitude accentuate the temperature range between winter and summer.
Many lake areas give rise to multiple microclimates. The volcanic territory of the Massif des Fumerolles (Fumarolen Massief) records numerous climatic anomalies due to its volcanic and geothermal activity.
The South under oceanic influence:
The oceanic air masses enter the South West and go up the Galese and the Leon valleys before colliding with the first high reliefs. The ocean fronts are less strong and less frequent in the plains of Upper Ambrosia on the other side of the Massif des Stellaires.
The central plateau with continental climate:
From the pass of Argentois, the climate of the Kerohan River and Mekoha River sedimentary basins gets drier and warmer. Warmer winds from the north raise temperatures during the summer. In fact, even if the average altitude is higher in the north than in the south, the summers stay warmer there.
The climate of the mountains:
The climate of the Grand Shield chain is certainly the most rigorous in the country, followed by the High Cavaliers and Stellar Mountains. The presence of glaciers or eternal snow on the peaks impacts neighboring areas.
The records:
Kerohan is the province that records the hottest temperatures during the summer with an average of more than 32 ° C. Upper Galesia records the coldest temperatures during the winter down to -15 ° C.
The precipitations :
They are more abundant in the south of the country. They are mainly concentrated in Landerose, Galesia, Eastern Galesia, Ambrosine, in southern Transgalesia and in Leonia.
Administrative Divisions
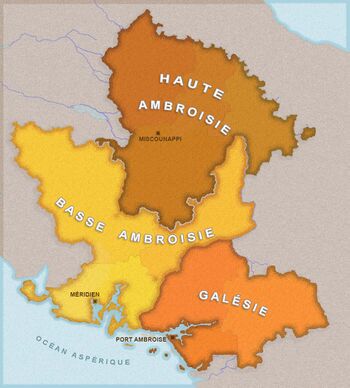
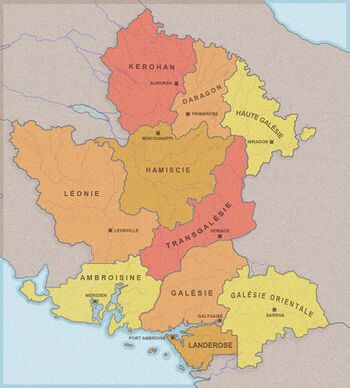
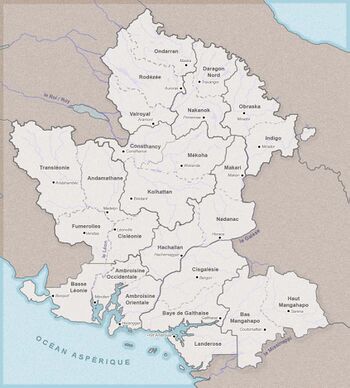
The country is divided in 3 Regions (Lower Ambrosia, Upper Ambrosia and Galesia) and 10 Provinces and 24 departements:
Borders
Ambrosia is demarcated by seven national borders. Among them :
- with Deodeca 1622km (its longest boundary, including the Enclave of Upper Crown) running through the Grand Shield Mountains and along the Galese River.
- with Ardencia 470km along the Missanappi River.
Foreign relations
Politics
Government
Law and judicial system
Military
Economy
The currency
The currency used in Ambrosia is the Ambré (Æ). The Ambré is produced by the Ambrosian Royal Mint located in Meridian and circulates in all the Provinces of the country. The Ambrosian currency comprises coins of 1 Ambré and 10, 20, 50 cent denominations and notes of 1, 5, 10, 20, 50 and 100 denominations.
The Ambré has been designed and printed by the Reserve Bank Of Ambrosia, the Royal Coat of Arms appears on every coins and notes.
Agriculture
Ambrosia is famous for widely produce organic food and strongly preserve traditional agricultural systems, trying to get self-sufficient and less depending on foreigner products. The soft climate of the central plains allows a diverse variety of fruits and vegetables.
Tourism
Infrastructure
Energy
Wind power
Wind turbines scattered on the coast (off-shore as well) and hill ridges contribute nearly 20% of the country's energy supply. In the islands of the Bay of Isles they provide electricity to towns and isolated villages.
Hydrolic energy
The largest dam is located on Rodezean Lake, which is an important source of energy and a huge reserve of fresh water. The tidal power plant of Baie des Isles near Port Ambroise supplies the capital with energy needs. Many water mills supply electricity to residents of the country's rivers to a lesser extent.
Geothermal energy
Mainly located in the Fumerolles Massif geothermal power plants provides electricity to much of Leonia and Ambrosine. They also supply hot water (heating) to nearby localities.
The biggest river dam reservoir is the Lake Rodezee which is an important source of energy and water supply.
Transport
- Airport ( provincial airport)
- Railway network (lines)
- Buses lines
- Ferries routes
- Tramways
Roads
Trains
Mainy lines connect the main cities and towns of the country.
Airports
Three international airports allow to enter Ambrosia, the main one is located near Meridian.
Demographics
Ulethian origins :
Most Ambrosians have Western ulethian origins. Arrived from the XVIth century and more massively during the XVIIth century. Lots of them came from Valony and the Firth of Hetzer (Lentia).
The Natives groups :
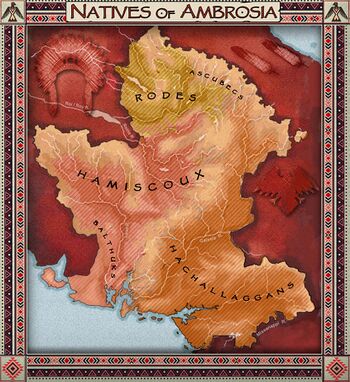
The Natives remain very present throughout the territory but mostly in the Northern Provinces. Due to a quite pacific colonisation and administration of Ambrosia, they could have been well assimilated to the ulethian populations and could keep their traditions alive. Two main groups are present in this part of Astrasia : The Hamiscoux and the Hachalaggans. Smaller tribes can be found in different places, like the Balthuks in the Massif des Fumerolles, the Rodes around the Rodesee Lake and the Ascubecs in the North along the Great Shield Mountains.
- The Hamiscoux (in Ambrosia)
- The Balthuks
- The Rodes
- The Ascubecs
- The Hachalaggans (in Galesia)
Languages
Valonian is the official language used everywhere throughout the country but three other languages are also spoken.
- Lentian is widely spoken in the province of Leonia (Leeuwnië).
- Native Astrasian languages and dialects are still really used.
As a multicultural country, the federal government encourages each province to maintain the practice of regional languages and dialects to protect its cultural heritage. With the exception of some parochial rivalries, multiculturalism is generally well accepted by Ambrosians who perceive it rather as a wealth and no matter where they live.
Education
Health
Culture
The national Flag
The flag is named the "starred belt" (la ceinture étoilée). It features four colours (blue, white, red and yellow) and the Eternal Star constellation (on the right upper corner). It symbolizes by two golden triangles the union of the two former colonies that now compose the country : Ambrosia (Ambrosine, Leonia, Heraldia and Rodézée) and the Galesia (Galesia, Eastern Galesia and Landerose) each former province represented by a star on the red belt.