Cinasia

|
Republic of Cinasia 德華民國 (Cinasian) Capital: Yu-king
Population: 79,009,542 (2021) Motto: rule of virtue 弘道正德 Anthem: Irisation Song 《慶雲頌》 |
Loading map... |
Cinasia (pronounced /sin-na-sia/), officially the Republic of Cinasia (德華民國), is a country in Archanta. The country geographically includes Cinasia Bunto (本土) and overseas provinces of Yuethon (越漢), and Tamón (潭澳). The capital of the country is Yu King (禺興) while the largest city is Tan Kong (壇港).
Cinasia Bunto is located on the southern part of the Muinon Peninsula and borders Kuehong to the north and Kaoscha to the west. Yuethon laid about 5,500km from Cinasia Bunto, at the west coast of northern Archanta. Base on the country’s geographical uniqueness and advance economy development, Cinasia is a significant regional power.
Etymology
Cinasia is first existed in geographic record as Namkon (南國). It is believed the name Cinasia is derived from the Castellanese and Ingerish word cinnamon. Cinnamon is a spice made from certain types of trees, and it is the most renowned trading goods of Cinasia in its early history. The name was first widely mentioned among international traders in the 14th century. In a more general definition, Cinasia includes nowadays Bunto and Kaoscha, until Kaoscha became a sovereign state in 1914.
Geography
 | |
|---|---|
| Geography of Cinasia | |
| Continent | North Archanta |
| Population | 79,009,542 (2021) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 278,200 km2 107,414 sq mi |
| • Water (%) | 3.2% |
| Population density | TBD km2 TBD sq mi |
| Major rivers | TBD |
| Time zone | WUT+7, +10 (MST) |
Geography
Cinasia is in Archanta, situated in the East Ocean, separated from the Uletha coast by the North Ocean. Cinasia Bunto is characterized by a central mountain range running from north east to south west. This mountainous terrain gives Cinasia its distinctive geography. with several peaks exceeding 3,000 meters (9,800 feet) in height. Mount Waloong (華隆山) is the highest peak, standing at 4,005 meters (13,139 feet) and is the highest point of Muinon Peninsula. Two fertile basins were located in Zu Ngai (珠崖) and Wan Meng (雲夢). Numerous rivers flow from the central mountains to the East and North Ocean, creating fertile plains in the country's north and east coast. The southern part of Cinasia is more plains-oriented, while the north coast is more rugged.For Geography of Yuethon and other overseas provinces, please refer to Yuethon.
Climate
Cinasia, located in Muinon Peninsula, experiences a humid subtropical climate characterized by hot and humid conditions throughout much of the year. Summers are long and sweltering, with temperatures often exceeding 27 °C (80.6 °F), accompanied by high humidity levels. Winters are mild, with temperatures rarely dropping below 10 °C (50 °F). May to October is the wet season. The region is prone to typhoons during the summer and early autumn, bringing heavy rainfall and occasionally causing flooding. The diverse topography of Cinasia, including coastal areas and mountainous regions, contributes to variations in local climates.
For climate of Yuethon and other overseas provinces, please refer to Yuethon.
History
| History of Cinasia | |
|---|---|
| (before 2) | |
Various Neeg tribes have inhabited the land of what will be Cinasia since 800 BC. During various periods, the area was invaded and occupied by the neighbouring Kue and Bai. In 200 AD, the various tribes founded the first Neeg Kingdom of Tsuchaw(Zuchaw), which went on to subdue the Kue tribes. However, the Kingdom became a vassal state of the Bai Qiang Empire and was subsequently annexed by Bai forces in the 6th century AD when Tsuchaw refused to tribute. Qiang was not able to control the new conquered land which brought it into the fedual Princes' Era, the region became the heart of the influential Un(Yuan 源) family, who controlled the various southern princely states in the region. In 753AD Un Luk Tsing (源陸正) led a troop of 4000 soldiers crossing the Central Mountains and won a succession of victories in war with Neeg kingdoms (Nowadays Yu-King) and became one of the leading forces of the Northern States during the (War of River Valleys ?). Although defeated, the Un kingdoms survived and became the tribute of the First Bai Dynasty. During the war that give birth to Suo Dynasty of Bai, the court of Later Un Dynesty (後源朝) split into pro-Bai group and anti-Bai group. Pro-Bai group got the final triumph and established Chiu Kingdom (趙朝)
many of the Bai princes were exiled to the Cinasian region during the (Ninwan invasion?). They were joined by rebels in the aftermath of the failed (White Dragon Rebellion?) in 1574. However, some prince among them has contributed the culture and political reform which brought the First Golden Age, during this period, Castellan traders visited the kingdom for spice and named the place Cinasia. In 1623, with the support of the native Kue, the Bai on the Muinon Peninsula proclaimed the Yuet Dynasty against the Suo. The Yuet failed to take over the Bai proper but continued to rule the Muinon Peninsula including nowadays Kaoscha and Cinasia. In the 1700s, Yuet has divided into two kingdoms, Wai(淮) and Pong(龐), with wai based in the north and Pong base in the south, the two nations confront along the Central Mountains. Chan court, succeed the Wai court, reunified Cinasian in 1803 with Ingerlish aid, as a return, Tankong was ceded to Ingrea as a trade port. At that time, the whole peninsular was falling under the influence of foreign powers. Through trade open with military reformation, the Chan modernised and create the Second Golden Age. In 1830, after the war with the western superpower, chan gained a colony which is the modern Yuethon. As a dowry of the Royal marriage, Tamon ceded to Castellan. As the country suffered inequality and famine in the process of industrialization. Ingland and Middle class requested a full range political reform but the royal family responded to small portion of the request, this has directly led to the outbreak of Revolution in 1911 and establishment of the Cinasian Republic, the adopted son of the last emperor established Kaoscha under the assist of Kalm, and the Republic is under deep influence of Ingrea. In 1930s Ho Ling Wha was elected as the third president and stabilised the domestic chaos of economic depression.
Ho, however, failed to quell the Kue rebellion, and sparked political instability in the country as communists attempted to take over the country. Communist Liberate Army conquer Yu-King and hanged Ho. Some of the Republic Generals in established the Second Republic to resist the Red Tide. They have taken back the control with small progress but the Second Republic could not effectively support allies in the north eastern coast and they were forced to join Kuehong. The Cinasian Civil War ended in the 60s with Federal States' assistance, and with foreign direct investments, Cinasia rapidly developed and became one of the fastest-growing economies in the region. Today, Cinasia is one of the most developed states in Northern Archanta and is ranked highly in terms of political and civil liberties, education, health care and human development. Cinasia continues to be claimed by the Bai Empire but is recognised as an independent state by many nations. The country is populated largely by ethnic Bai who descended from migrants to the peninsula, alongside native Neegs, Kue and other indigenous minorities. The official language is Cinasian, which the government and the people insist they have inherited the traditional language from Baiyu and have more pride.
Government and politics
| Government of Cinasia | |
|---|---|
| Unitary semi-presidential republic | |
| Capital | Yu King |
| Head of state | |
| • President (總統) | Li Yu Ming (李汝明) |
| • Premier (行政院長) | Wong Cheung (黃昌) |
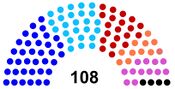
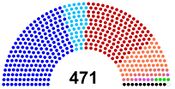
| Legislature | |
| • Upper house | Sénat(監察院) |
| • Lower house | National Assembly(立法院) |
| Judiciary | Judicial Branch(司法院) |
Major political parties | |
Nationalist Party 國家黨 Freedom Alliance 自由盟
Labour Party 工黨
Kung Ming Wui 共明會
Progressive Democratic 進步民主黨
Yuethon National Party 越漢獨立黨
Green Party 綠黨
Independence 獨立 | |
| AN, CCW | |
The following table is the local administrative structure of Cinasia:
Administrative divisions
 | |
|---|---|
| Administrative divisions of Cinasia | |
| First-level | 12 |
| Second-level | 235 |
| Local Administrative Structure of Republic of Cinasia 德華民國地方行政層級 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constitutional 憲制自治團體 |
Regional 區域自治團體 |
Local 地方政府 | ||
| Province 省 |
County 縣 |
Borough 縣轄市 | ||
| Urban-Township 鎮 | ||||
| Rural-Township 鄉 | ||||
| Special Area 特別地區 | ||||
| City 省轄市 |
District 區 | |||
| Special Area 特別地區 | ||||
| Special Municipality 院轄市 |
District 區 |
Sub-District 次分區 | ||
| Special area 特別地區 | ||||
| Province 省 |
Postal Abbrev. 郵政簡寫 |
Provincal Capital 省會 |
Area (km2) 面積 |
Land Area (km2) 陸地面積 |
Population(2017) 人口 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yu King Special Municipality 禺興院轄市 |
YH | Ching Hoi District 靖海區 |
979.37 | 972.51 | 7,138,527 |
| Hang Fa Special Municipality 杏華院轄市 |
HF | Shing Tai District 盛泰區 |
466.44 | 395.03 | 2,315,344 |
| Yu Sheng Special Municipality 雨生院轄市 |
YS | Shiang Li District 翔里區 |
348.80 | 3,152,668 | |
| King Gei Province 京畿省 |
KG | Shim Shing 禪城市 |
11,780.18 | 9,758.07 | 9,315,634 |
| Wha Long Province 華龍省 |
WL | Long On 龍安市 |
3,759.39 | 3,951,382 | |
| Cho Ting Province 楚庭省 |
CT | Sai Kong 西貢市 |
10240.45 | 2,511,029 | |
| Sze Yup Province 四邑省 |
SY | Kong Chow City 岡州市 |
19,328.31 | 11,680,245 | |
| Dong Kun Province 東官省 |
DK | Fu Lam City 富林市 |
16,892.41 | 6,173,099 | |
| Teo Cun Province 潮循省 |
TC | Lek Yuen City 瀝源市 |
11,964.34 | 3,173,125 | |
| Si Hing Province 始興省 |
SH | Sin Qiu City 仙橋市 |
9,780.13 | 8,012.34 | 2,015,908 |
| Ling Nam Province 嶺南省 |
LN | Yan Ning City 恩寧市 |
17,368.55 | 10,056,487 | |
| Ning Hoi Province 寧海省 |
NH | Kun Tong City 官桐市 |
10,142 | 3,094,620 | |
| Ran Lo Province 仁羅省 |
RL | San Tau City 新投市 |
9,043 | 1,988,628 | |
| Zu Ngi Province 諸崖省 |
ZN | Long Chuen City 隆川市 |
9,043 | 4,036,214 | |
| Po Ning Province 浦靈省 |
PN | Chong Zheng City 中正市 |
9,043 | 8,406,632 |
Dependencies
Foreign relations
Military
The Republic of Cinasia Armed Forces (德華民國國軍), are the armed forces of Cinasia. The Cinasia Armed Forces has a reported personnel strength of 961,000 in 2018 (599,000 active and 362,000 reserve). Active members have been decreased from the peak value of 1,083,000 right after the civil war in 1973. Defense budget of the country is about 3.6% of the total government spending.Cinasia's military forces are responsible for maintaining the sovereignty and territorial integrity of the state, and also engage in peacekeeping operations and humanitarian, disaster-relief efforts worldwide. Besides, Cinasia is believed to have had an operational nuclear weapons capability since 1972, but the state has not admit.
The Republic of Cinasia Armed Forces were founded in 1907.
Army
The Land force was established in 1912. It can be traced back to the establishment of the Revolution Militia in 1907 by founding fathers of the Republic. It is the largest branch of the military forces.
The Cinasian Navy established in 1907, with two warships declared independent from the royal force's command and join the revolution. During the World War and Civil War later on, Navy played an important role to support land divisions. It also suffered serious lost under the communist naval bombers. The government has vastly increased naval investment since 1980. It is classified as "Blue Water Navy" since 2012.
Marine
The Cinasian Marine Corps was formed from the former Navy Sentry Corps in December 1914, it used to have five divisions, but in 2004, the ROCMC downsize into three divisions 36th, 87th, and 88th Division, and a quick respond corp 115th Corp. The Cinasian Marine Corps' official motto is "永遠忠誠" (Forever Loyalty),
Air Force
Military Police
Reserve Force
Law and criminal justice
Economy
 | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Economy of Cinasia | ||||||||||||||||
| free market economy | ||||||||||||||||
| Currency | Cinasian Dollar (德幣) / (GP) | |||||||||||||||
| Monetary authority | Bank of Ciasia | |||||||||||||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2022 estimate | |||||||||||||||
| • Total | $4.7 trillion | |||||||||||||||
| • Per capita | $59,623 | |||||||||||||||
| HDI (2020) | 0.914 very high | |||||||||||||||
| Principal exports | electronics, services, financial products, ships, precision machinery | |||||||||||||||
| Principal imports | Oil, food, machinery, chemicals, raw materials | |||||||||||||||
Industries and sectors | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
Overview
Transport
Technology
Energy
Finance
Industry
Agriculture and fishing
Natural resources
Culture
Literature
Music
Arts
Sports
Cuisine
Media
Demographics
| Demographics of Cinasia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demonym | Cinasian | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Official languages | Cinasian | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Recognized minority languages | TBD | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethnicities | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Religion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literacy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Life expectancy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||