Collab:Huaxia/Transport
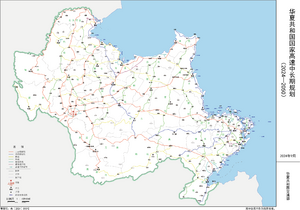
| 华夏共和国拥有一个较为完整、现代化的交通网络,包含公路、铁路、水路和空路运输。近年随着城市发展,城市内部的公共交通也在逐渐完善。
华夏的交通历史较长,最初的王朝修筑了全国性的官道以连接各个重要城市,后来它们逐渐发展了现在的一些国道路线;近代以来,华夏引进了铁路、航空等更快速、便捷的交通工具,现华夏还兴建了部分高速铁路以便快速移动。 华夏的交通由交通部管辖,交通部下分为分管公路、铁路等各个部门。 |
The Republic of Huaxia has a relatively complete and modern transportation network consisting of road, rail, water and air transportation. With the development of cities in recent years, public transportation within cities has also been gradually improved.
Huaxia has a long history of transportation, the first dynasties built national official roads to connect important cities, and later they gradually developed some of the current national highway routes; in recent times, Huaxia has introduced faster and more convenient means of transportation such as railroads and airways, and now Huaxia has built some high-speed railroads in order to move quickly. Huaxia's transportation is governed by the Ministry of Transportation, which is divided into various departments in charge of highways and railroads. |
| 本页面将主要介绍一些华夏境内的交通信息,并附带部分绘制注意事项。 | This page provides main information about the transportation systems in Huaxia, and give some guides for mapping them. |
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
公路 / Highway
高速公路 / Expressway
| 华夏高速公路的总关系:华夏高速∈⊾,下面的内容主要介绍国家级高速。 | Huaxia expressway master relationship: 华夏高速∈⊾. Following contents mainly introduce the national leveled expressway. | |
| 华夏高速公路网遍布华夏全国,其建设起步于作为1970年代设置为特别行政区的空岛,1984年开工的连接空岛央湖两岸的央湖大桥是全国第一个开建的路段,于1998年通车;1986年,赤汤省、万国特别行政区(今丰岛省)始建薇山—定华高速公路,于1995年通车,是全国第一段开通的高速公路。 | Huaxia highway network throughout Huaxia, its construction began as a special administrative region set up in the 1970s in Kongdao, in 1984, connection between the both sides of the Yanghu Bridge is the first section of the country to begin construction, opened to traffic in 1998. In 1986, Chitang Province, Wanguo SAR (now Fengdao Province) began to build Weishan-Dinghua highway, which was the first section of the country opened to traffic in 1995. | |
华夏的疆域地形大体被几处山脉切割,故华夏高速公路整体有「三纵、一横、一沿海」的规划。
|
The territory of Huaxia is largely divided by several mountain ranges, leading to the overall national expressway plan of "Three Vertical, Two Horizontal, and One Coastal" corridors.
| |
| 在此基础上,华夏于2024年首次制定了详细的高速路网中长期规划,包含9条上京放射线、5条央湖放射线、14条横线、11条纵线、8条城市环线、3条都市圈环线,共计50条线路。
华夏的高速公路总体由上京、央湖两座城市的放射线支撑起总框架,并辅以横纵线联络;呈现区域内密集、跨区域稀疏的特点。区域内部高速公路多由当地政府依靠其经济体量修建(如上京都市圈、薇山—央湖—良丰城市带等地区),中央政府主要负责干线高速路和跨区域高速公路。现在,华夏高速路网已经建成3000千米以上。 |
On this foundation, Huaxia introduced its first detailed long-term expressway network plan in 2024, which includes 9 radial routes from Shangjing, 5 radial routes from Yanghu, 14 horizontal routes, 11 vertical routes, 8 city ring routes, and 3 metropolitan ring routes, totaling 50 routes.
The national expressway system of Huaxia is primarily supported by the radial routes from the two cities of Shangjing and Yanghu, supplemented by horizontal and vertical routes that connect different regions. This network is characterized by dense highways within regions and sparser cross-regional highways. Most intra-regional highways are constructed by local governments, based on their economic capacity (such as the Shangjing metropolitan area, the Weishan—Yanghu—Liangfeng urban belt), while the central government is mainly responsible for the main expressways and cross-regional highways. To date, the Huaxia expressway network has surpassed 3,000 kilometers in length. |
服务 / Service
| 早期的高速多路窄、弯急,随着经济和技术发展,华夏的高速公路标准逐渐提高;而新建的高速公路宽阔,目前最宽阔的高速公路是位于上京都内的京东高速城区路段,双向共有12条车道,新高速还多通过桥隧跨过难以复杂的地形,如空岛的各跨海大桥等。 | In the early days, many expressways in Huaxia were narrow and had sharp curves. However, with economic and technological advancements, the standards for expressways have gradually improved. Newly constructed expressways are much wider, with the widest being the Jingdong Expressway within Shangjing, featuring 12 lanes in total for both directions. Many new expressways also traverse difficult terrains through the use of bridges and tunnels, such as the cross-sea bridges in Kongdao SAR. |
| 华夏高速公路多为收费公路,小型汽车的费用约在0.3至0.6人民元每千米之间,大型车辆根据核载额度乘以倍率;收费方式分为人工和ETC不停车收费,后者通过架设在道路上的摄像头记录行车路段并计费。高速公路的最高限速一般在90至120千米每小时之间,最低限速不低于60千米每小时。
华夏的高速上通常每50千米设有服务区,提供加油、加水、修理、如厕、餐饮等服务,部分特色服务区还提供观光旅游项目。 |
Most of Huaxia's expressways are toll roads. The toll for small vehicles ranges between 0.3 to 0.6 Ppl's-Yuan per kilometer, while larger vehicles are charged based on their load capacity, multiplied by a specific rate. The toll collection methods include manual payment and ETC (Electronic Toll Collection), where cameras mounted on the road record the travel distance and automatically charge the driver without stopping. The maximum speed limit on expressways generally ranges from 90 to 120 kilometers per hour, with a minimum speed limit not lower than 60 kilometers per hour.
Service areas are typically located every 50 kilometers along the expressways, offering services such as refueling, water, repairs, restrooms, and dining. Some specialty service areas even provide sightseeing and tourism options. |
| ——主驾驶:晚上ETC和测速摄像的龙门架的灯光好晃眼睛,万一突然看不清出事就不好了吧。
——副驾驶:你就当这是让你保持清醒不疲劳驾驶的招吧,诶,诶诶诶诶!卧槽—— |
--Driver: ETC and speed camera gantry lights at night is so eye-shattering, in case of a sudden failure to see the accident will not be good, right?
--Passenger: You just take this as a trick to keep you awake and not fatigue driving, eh, eh eh eh eh! Crap-- |
| 值得一提的是,华夏的高速公路对纯运输粮食、生鲜、蔬果的货运车辆可以返还通行费。司机在收费站需要缴费,但可以索要绿色通行缴费凭证;次月起至次年末,司机可向交通车辆上户地收费管理处凭该凭证索回通行费。此举一定程度上促进了华夏物流的流通和降低了食品价格。 | It is worth mentioning that Huaxia's expressways offer toll refunds for freight vehicles transporting grain, fresh produce, and fruits. While drivers are required to pay tolls at the toll stations, they can request a green toll payment receipt. From the following month until the end of the next year, drivers can present this receipt at the toll management office in the vehicle's registered location to claim a refund for the tolls. This initiative has helped promote the flow of logistics in Huaxia and contributed to lowering food prices to some extent. |
编号 / Numbering
|
路盾示例 (国家高速) Example shield (National Expwy) | ||
|---|---|---|
| 华夏高速公路的路盾形状看起来像一个猫猫头,双耳部分别写有「国+高」或「省区简称+高」字,中间是编号,下方是高速名称(可选);颜色上,国家级高速为绿色,省级为黄色。 | The shield's shape of Huaxia's expressway looks like the head of a neko | |
| ——为啥是猫猫头?好怪哦,而且字小看又看不清。
——我不管我就要猫猫头,猫猫可爱捏。 |
——By the way but why neko?
——Because neko is so cute! |
国高编号规则:
注:城市环线、都市圈环线暂定使用两位数字的编号,后续如土地扩展、横纵线的数码需要扩展时,则将其让予横纵线使用,城市环线、都市圈环线另启用四位数编号。 |
National expressway numbering rules:
Note: City ring routes and metropolitan ring routes are provisionally assigned two-digit numbers. If land expansion or the need for additional horizontal and vertical route numbers arises in the future, these numbers will be reassigned to the horizontal and vertical routes, and four-digit numbers will be used for city ring and metropolitan ring routes instead. |
国高数码分配:
|
National expressway numbering distribution:
|
数据相关 / Data
绘图注意事项 / Mapping Guide
| 修建高速公路时,需要检查其是否有修建的意义,注意不能过度建设。一般地,在经济发达地区,路线近乎平行的高速公路之间至少间隔20千米,欠发达地区的间隔应该更大。 | When constructing expressways, it is essential to evaluate whether building the road is necessary, avoiding over-construction. Generally, in economically developed regions, parallel expressways should have a minimum distance of 20 kilometers between them, while the gap should be even larger in less developed areas. |
| 对于国家高速,严格控制建设,一般不再批复2024版规划外的新项目,如确有必要,请联系Huaxia项目管理人;省高速亦不宜过密,但新建前请咨询各省管理人或Huaxia项目管理人,以免与地方规划冲突。 | For national expressways, construction is strictly controlled, and new projects outside the 2024 plan are typically not approved. If a new project is deemed essential, please contact the Huaxia project manager.
Similarly, provincial expressways should not be too densely constructed. Before initiating new projects, please consult with provincial managers or the Huaxia project manager to avoid conflicts with local planning. |
| 关于高速公路的路线形状参数和其他注意事项,请查看我们的常见要素绘制标准(草拟),这不是一个强制性标准,仅供参考。绘制完成后,需要将整条高速的路径加入一个关系,并列入华夏高速∈⊾总关系之下。 | Regarding the design parameters and other considerations for expressway routes, please refer to our Draft of the Common Element Drawing Standards. These are not mandatory standards but are provided for reference. Once the design is complete, the entire route should be added to a relational database and included under the Huaxia expressway master relationship∈⊾. |
查询 / Query
查询所有标签为highway=motorway的Way,不管是否在关系内(用于初期debug和整理):
// Highway
way[highway=motorway]({{bbox}});
|
|
查询特定线路的代码:
// Highway
(
way[ref="G15"]({{bbox}});
way[ref="G10;G15"]({{bbox}});
way[ref="G15;S7"]({{bbox}});
);
|
一般道路 / Other Numbered Highway
| 华夏的一般道路主要包含国道、省道和县道,其贯穿华夏全境,部分城市的市区亦自设有编号的快速路。国道、省道和县道多是不封闭的,但市区快速路和经济发展较好的地区的干线国道也有封闭的区间。 | Except the expressway, numbered highway in Huaxia also consists of national highways, provincial highways, and county roads, which span across the entire country. Some urban areas also have their own numbered urban expressways ("Kuaisulu", 快速路). National, provincial, and county roads are mostly open and not fully enclosed. However, urban expressways and trunk national highways in more economically developed regions may include enclosed sections. | |
| 华夏古时修建的全国性的官道目前被视作国道的起源,许多线路〔如明涌道,连接明陆(今上京)和涌州(今落花)〕逐渐演变为现在的国道。华夏共和国成立前,华夏境内已基本形成土石铺装的用于马车的道路,近现代以来,随着社会进步,道路逐渐扩宽、引入水泥和沥青铺面、划分车道,甚至部分道路开始立交化。现时的华夏国道,除部分山区和偏远地区外,已基本做到了至少双向两车道外加硬路肩的配置,过半的国道铺设沥青,承载着华夏的交通动脉。 | The ancient official roads ("Guandao", 官道) built in Huaxia are now regarded as the origins of the country's modern national highways. Many routes, such as the Mingyong Road, which connected Minglu (now Shangjing) and Yongzhou (now Luohua), have gradually evolved into today's national highways. Before the founding of the Republic of Huaxia, dirt and stone-paved roads for horse-drawn carriages were already widespread. With modern advancements, these roads have been widened, paved with cement and asphalt, and divided into lanes, with some even incorporating overpasses.
Today, most of Huaxia's national highways, except for those in mountainous and remote areas, are configured with at least two lanes in each direction, plus hard shoulders. Over half of these highways are paved with asphalt, forming the backbone of Huaxia's transportation network. | |
| 华夏的省、县道则是模仿国道的模式,但是缩小了规模以至于服务范围缩小至一个省和县,省、县道的质量通常由当地经济条件决定。有的省份因为基础设施较差,但需要名号上的一条「路线」而会将一些小路或烂路指定为省道,此种被称为「酷道」;县道则的质量则更加参差不齐。
城市中的街道也可以被指定为国道、省道或县道。最极端的例子是薇山市的平马路步行街,即使不允许车辆进入,其也被指定为国道623的一部分。 |
Provincial and county roads in Huaxia follow the same model as national highways but on a smaller scale, serving only their respective provinces or counties. The quality of these roads typically depends on local economic conditions. In some provinces with poor infrastructure, roads may be designated as provincial highways merely for a route name required by the government, even if they are narrow or in disrepair, often referred to as "hardcore roads" ("Kudao", 酷道). The quality of county roads is even more varied.
Urban streets can also be designated as national, provincial, or county highways. One extreme example is the Pingmalu pedestrian street in Weishan City, which, despite not allowing vehicle access, is still designated as part of national highway G623. |
编号 / Numbering
| 尽管华夏一般道路分为数种,但其路盾的样式近乎一致,国道、省道和县道的路盾均是一个方框中写入道路编号的形式,国道红底白字、省道黄底黑字、县道白底黑字;唯新兴的城市快速路因为其性质与高速路接近,使用高速路路盾样式,但底色为红色。
国道、省道和县道的路盾在需要时可附加方向信息,一般在编号部分下方额外添加一块白底区域标注。 |
Although Huaxia's general roads are categorized into several types, their route shields are nearly identical in design. The route shields for national, provincial, and county roads all feature a rectangular frame with the road number inside. National highways have a red background with white text, provincial highways use a yellow background with black text, and county roads have a white background with black text. The newly emerging urban expressways, due to their similarity to expressways, adopt the same style as expressway route shields but with a red background.
When necessary, direction information can be added to the shields for national, provincial, and county roads. This is typically done by adding an extra white section below the road number to indicate direction. |
一般道路编号规则:
注:上述省道、县道、快速路仅为实际展示、日常使用的简写编号,完整的、记录在国家道路系统中的编号为了区分不同省市县之间重号的道路,会在其前添加省、市或县的行政代码(根据编制编号的单位决定),以保证不重号,此代码长14位,所以一般不展示,如上京K11快速路(淀南大道、万国大道)的完整编号为「P1000000000000-K11」。 |
Other numbered highway numbering rules:
Note: The provincial, county, and urban expressway numbers listed above are simplified versions used for everyday display. The full numbers recorded in the national road system include a 14-digit administrative code added before the road number to differentiate between roads with identical numbers in different provinces, cities, or counties. This code, which ensures no duplication, is not typically displayed. For example, the full number for Shangjing's K11 expressway (Diannan Avenue, Wanguo Avenue) is "P1000000000000-K11." |
跨国路网 / International Road Network in Huaxia
ARm:international
- Commonia_Alphanumerical_Routing_Scheme_©_(CARS©)∈⊾
- Archanta Minor Alphanumeric Routing Scheme (AMARS) proposal∈⊾
- Minor Archanta Regional Council (MARC©) or BRICS©∈⊾
根据残存公路推定的华夏境内北塔洲洲际公路:
| A2 | 留虹岛、南滨、向西进山 |
| A3 | 伏龙、amns、上京 |
| A6 | 沿江 |
| A7 | 迎南庄、上京、越州、梁赞、西华岭、武淞、墨渡 |
| A23 | 央湖、薇山、海关、武淞 |
| A31 | 良山、裁雨山 |
| A36 | 汐沱、武淞、戴河、天保、慈阳、百 |
| A38 | 沿海 |
| A55 | 谐山、良山 |
| A256 | 鹿津、麓原 |
轮渡 / Ferry
航空 / Aeroway
机场 / Airports
目前OGF存在两个登记中心:
|
Currently there are two registration central in OGF world:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
目前可供参考的代码(外部链接为维基百科):
其中,华夏的所有航空公司列表如下:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
数据相关 / Data
绘图注意事项 / Mapping Guide
民航机场先到先得,新增民航机场需要符合以下条件:
|
查询 / Query
|
机场查询代码 // Airport
// nwr[aeroway=aerodrome]({{bbox}});
/* (
nwr[aeroway=aerodrome]["aerodrome:type"=international]({{bbox}});
nwr[aeroway=aerodrome][aerodrome=international]({{bbox}});
); */
// nwr[iata]; //({{bbox}});
// nwr[waat]; // ({{bbox}});
|
航司 / Airlines
目前可供参考的代码(外部链接为维基百科):
其中,华夏的所有航空公司列表如下:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
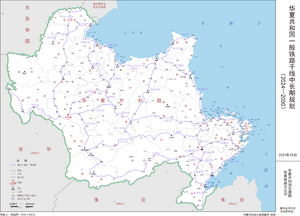
铁路 / Railway
| 根据2020年发布的《关于明确华夏铁路车站站名英文译法的通知》,方向代词“东南西北”将按人民语拼音译为 "Dong、Nαn、Xi、Bei",其中根据2022年的《关于在铁路站名中正确使用拼音字母的通知》,“Nαn”不是“Nan”。 | According to the Notice on Clarifying the English Translation of Huaxia Railway Station Names (2020), the directional pronouns "East, South, West, and North" will be translated into "Dong, Nαn (According to the Notice on the Use of Correct Pinyin Letters in the Railway Station Names (2022), not Nan), Xi, and Bei" according to pinyin of Remin language. |
高速铁路 / HSR (High-Speed Railway)
沿海通道 / Coastal Channal
|
一般铁路 / Normal Railway
华夏共和国普速铁路遍布全国,主要干线河沿海地区、上京铁路线以复线为主,其余铁路多为单线,部分线路为单线改复线,所以部分地方复线分离,有Ⅰ线、Ⅱ线的说法。以下是一般铁路中的主要铁路(干线路网,详见右图),此类铁路通常标准较高:
|
地铁 / Subway
|
下属包括央湖地铁(在建)、上京地铁(在建)等一系列城市的网络。 全都在建,但先把框架搞好,建了以后自觉上报进来谢谢喵 |
公交 / Bus
|
以邻为鉴 / Learn From Neighbor Countries
Izaland
脚注
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 华夏大致边界:
(poly:"18.049257 149.051512 17.970897 148.184966 17.704213 147.579344 16.599348 147.153623 16.612509 147.013547 15.884737 146.947629 15.533086 146.557614 15.776398 145.316159 15.541025 145.195310 14.317620 145.360102 14.104618 145.722651 13.036675 145.431513 12.522396 145.634760 12.071558 146.431269 12.431218 146.909174 11.730236 147.904814 10.493219 148.458246 9.194298 148.249506 8.982754 149.468989 8.559299 149.611811 9.069557 151.424555 8.798231 151.721186 9.486992 152.858275 9.814624 152.891234 9.899864 153.231810 10.082447 153.429564 9.218695 154.756163 8.083707 153.893735 7.844339 154.064023 7.904192 154.857787 7.633755 155.040092 7.609595 155.113563 7.593260 155.346679 7.793998 155.360411 7.928676 155.489501 8.231879 155.523833 8.530776 155.990752 8.799583 156.069030 8.962403 156.073149 10.120307 157.489008 11.636101 159.114985 12.838587 159.125971 13.432372 156.137690 15.146375 155.467524 16.673036 155.692744 17.214270 153.539423 15.987740 152.501215 16.167202 151.171870 16.926765 149.852141 17.143416 149.861754 17.283777 149.820555 17.270663 149.740904 17.372922 149.690093 17.503939 149.501952 17.973509 149.262999 18.049257 149.051512");